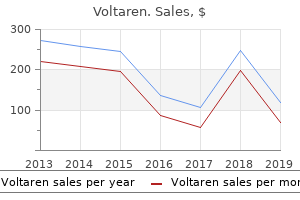
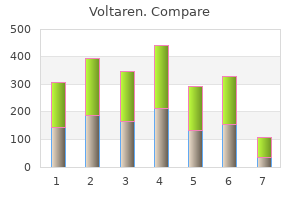
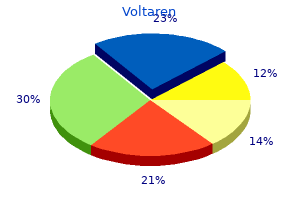
Voltaren"Voltaren 50mg overnight delivery, rheumatoid arthritis diet book". By: O. Dawson, M.B. B.A.O., M.B.B.Ch., Ph.D. Co-Director, California University of Science and Medicine Surgical exploration revealed an intact artery with an intimal tear and subsequent infarction of the kidney arthritis medication for gastric bypass patients order voltaren 100mg without a prescription. Today many of these early complications can be treated with percutaneous drainage procedures. All patients with renal trauma regardless of the initial stage should undergo immediate imaging studies if they develop prolonged or increasing abdominal pain, fever, nausea, hypotension, or hypertension. The late complications are similar to complications that occur early on, and include delayed hemorrhage, urinoma, hypertension, hydronephrosis, calculi, pseudoaneurysms, renal scars, and loss of renal function. A long-term study by Yale-Loehr and colleagues59 of five patients with severe renal trauma revealed the kidneys lost an average of 12% function because of trauma with a mean percentage of total renal function of 38%. Devascularized renal segments or entire kidneys need not be removed unless they cause problems. Most often the devascularized segment contracts along with the hematoma as the kidney heals. Abdalati and coworkers55 studied six children who had pedicle injuries with completely infarcted kidneys. One child acquired an infection that required removal of the dead kidney, and the remaining five recovered without surgery. It is important to follow these infarcted kidneys or renal segments with repeated imaging. If the patient does not recover rapidly or at any sign of infection, a nephrectomy or partial nephrectomy should be performed. Although gunshot wounds are the dominant form of renal injury, stabbing has become more common as a result of street violence. High-velocity gunshot wounds cause damage at a considerable distance from the point of impact. These injuries cause contusion of adjacent tissue, and the viability of this injured tissue is difficult to judge for days after injury until some reversible damage has begun to heal. Renal Stab Wounds the history and physical examination in patients with potential penetrating renal injuries offer more information to the examining physician than in blunt renal trauma. The weapon, the skin wound, and the location of the wound all offer helpful information about the potential renal injury. In all stabbings that could potentially injure the kidney-in the lateral abdomen, flank, or lateral back-the kidney is damaged in only 15%. The highest risk of injury to the kidney occurs when the patient is stabbed in the flank, the area between the anterior and posterior axillary lines. Eastham and coworkers11 reviewed 244 stabbings that could potentially injure the kidney, and found that 75% of all renal injuries resulted from stabbings in the flank, with only 12. Only 23% to 33% of stabbings cause major parenchymal injury, and another 23% cause significant vascular damage. Of patients with renal stab injuries, 12% to 43% have associated organ trauma, most commonly to liver, spleen, and colon. In a series of 244 patients who had stab wounds that could potentially involve the kidney, Eastham and associates11 found 46 with microhematuria and 14 with gross hematuria. Along with the position and appearance of the stab wound, other signs of potential renal stab injury include flank tenderness, a flank mass, and hemodynamic instability. There is almost uniform agreement that in unilateral blunt renal trauma, blood pressure and overall renal function are almost always normal when measured within the first few years after injury. The long-term effects on the injured kidney have been studied and are not as encouraging. Functional loss in the damaged kidney may be progressive over time in the case of severely traumatized kidneys. They looked for evidence of compensatory renal hypertrophy by the normal kidney and found none, worsening the long-term prognosis for global renal function. These findings indicate that despite normal blood pressure and overall renal function in children who sustain significant renal trauma in the first few years after injury, these injuries may lead to problems years later. We believe that children who sustain such injuries should undergolifelong blood pressure monitoring and routine urinalysis to look for proteinuria owing to renal deterioration. Angiography has been useful because of its accuracy in diagnosing vascular injuries and its potential usefulness as a therapeutic tool to control bleeding. Management of renal stab injuries has become progressively more conservative, and fewer patients need immediate surgery. The importance of accurate initial staging is shown by a study of 60 renal stab wounds managed with bed rest in which the complication rate was 20%.
Clinical findings of seminoma include either a painless testicular mass (usually on the right side) or a diffuse nodularity throughout the testis does arthritis in the knee come and go purchase voltaren 50 mg free shipping. Clinical findings of mumps viral infection include malaise, fever, and shaking chills. The incidence is increased when the testes are positioned horizontally and the tunica vaginalis is attached high on the spermatic cord ("bell clapper deformity"). Because the pampiniform venous plexus collapses more easily than the testicular artery, the testis becomes distended with blood and very painful. This is a medical emergency since compression of the testicular vessels results in ischemic necrosis with 6 hours. Skin consists of three layers: the outer epidermis, the middle dermis, and the deep hypodermis (or subcutaneous layer) that corresponds to the superficial fascia in gross anatomy. Skin is classified as thick skin (5 mm; covering the palms of the hand and soles of the feet) and thin skin (1 to 2 mm; covering the rest of the body). In addition, skin has a number of epidermal derivatives (or skin appendages), namely, hair, nails, eccrine sweat glands, apocrine sweat glands, and sebaceous glands. Skin has the following functions: regulation of body temperature, a water barrier, nonspecific barrier to microorganisms, excretion of salt, synthesis of vitamin D, and a sensory organ. A number of different cell types can be found in this epithelium as indicated here. Keratinocytes are arranged in five strata: basale, spinosum, granulosum, lucidum, and corneum. Melanocytes are clear cells that have long, branching cytoplasmic processes and are found in the stratum basale. When melanin synthesis is completed, the melanosome loses its tyrosinase activity and the melanosome is then called a melanin granule. Melanin granules are transferred to neighboring keratinocytes within the stratum basale and spinosum via cytoplasmic processes. They are in contact with sensory nerve fibers that project from the dermis into the epidermis and terminate in a platelike ending called the nerve plate. Langerhans Cells are antigen-presenting cells that have long, branching cytoplasmic processes and are found mainly in the stratum spinosum. A: Table of characteristics of keratinocytes within various strata of the epidermis. B, stratum basale; S, stratum spinosum; G, stratum granulosum; L, stratum lucidum; not shown in this section, C, stratum corneum. A Meissner corpuscle consists of flattened, disc-shaped epithelial cells (N) surrounded by a capsule (Ca). E: Diagram of skin appendages showing an eccrine sweat gland (Ec), apocrine sweat gland (Ap), sebaceous gland (S), and hair (H) with its associated arrector pili muscle (M). The dermis consists of connective tissue composed of fibroblasts, type I collagen, and elastic fibers. They regulate body temperature via postganglionic sympathetic neurons that use acetylcholine (cholinergic). Note: As a rule, postganglionic sympathetic neurons use norepinephrine as their neurotransmitter. They regulate emotional sweating via postganglionic sympathetic neurons that use norepinephrine (adrenergic). The secretory portion contains cells that secrete a viscous product via merocrine secretion. Modified apocrine sweat glands are found in the eyelids (glands of Moll) and external auditory meatus (ceruminous glands, which produce cerumen, i. Case selection by a skilled orthopedic oncologist arthritis in dogs how to treat generic voltaren 50 mg with visa, invocation of sound oncologic principles, and adequate rehabilitative services postoperatively are all necessary to achieve the best possible function and cancer control. Metastatic Disease Surgery also plays a role in treating osteosarcoma metastatic to the lung. Some patients present with a primary tumor along with limited pulmonary involvement. Aggressive multiagent chemotherapy, surgical management of the primary tumor, and thoracotomy for resection of pulmonary metastases appear to have significantly increased survival in cases that seemed hopeless (Table 10. The most common sites of metastases in the relapse of initially localized osteosarcoma are lung and bone. When tumor relapses in the lung, surgical resection of pulmonary nodules may result in a prolonged disease-free interval and, together with aggressive chemotherapy, a small potential for cure (6,25,30,29,44,55,56). In some patients, repeated thoracotomies appear to have prolonged survival in the face of multiple episodes of pulmonary metastases (43). Primary metastatic osteosarcoma: presentation and outcome of patients treated on neoadjuvant Cooperative Osteosarcoma Study Group protocols. Several variables must be considered when one uses metastasectomy for pulmonary metastases. These include the aggressiveness of the proposed operation, whether they are unilateral or bilateral, the interval between the development of the metastases and the treatment of the primary, the extent of vascular invasion, the presence or absence of hilar lymph node involvement, and whether additional salvage chemotherapy is available after surgery (48,49,57). The role of the bony metastasectomy is not well defined, undoubtedly because the occurrence of bony metastases in the setting of potentially salvageable osteosarcoma is far less common than that of pulmonary metastases (48). With mainly chemotherapy and surgery, the 5-year overall and event-free survival rates were 32% and 18% for second, 26% and 0% for third, 28% and 13% for fourth, and 53% and 0% for fifth recurrences, respectively. Radiation Therapy Prebiopsy Sweetnam (44) administered low-dose irradiation before the initial biopsy (approximately 10 Gy) to 29 patients in the hope of reducing the viability of cells that might be disseminated into the bloodstream by the biopsy. The 20% overall survival rate, no different from that of historic controls, discouraged additional investigation. Because the survival rate with surgical ablation alone was only 20%, many limbs were sacrificed in vain. Surgeons and radiotherapists reasoned that if high-dose local irradiation could obtain at least temporary control of the primary tumor, a time interval would be obtained that would allow the selection of cases suitable for a radical surgery. Those who did not develop pulmonary metastasis after the waiting period would undergo extirpation of the primary tumor. This philosophy was promulgated by English physician Sir Stanford Cade and is called the Cade technique. There generally was a reduction in pain and swelling at the tumor site after the first 20 Gy. This response tended to continue for several weeks after completion of radiotherapy. In patients who underwent limb ablation after radiotherapy, a histologic analysis could be performed to assess the presence or absence of viable tumor. There were some long-term survivors after aggressive treatment with radiation therapy alone (6,66). Modern Series of Primary Photon Radiation Therapy In modern radiotherapy practice, it is rare to be asked to use radiotherapy as the primary local treatment for osteosarcoma except for lesions in inaccessible sites. However, the data acquired with the Cade technique make it reasonable to consider the use of radiation in certain situations. His magnificent collection of scientific specimens was purchased by Parliament and placed in the custody of the Company of Surgeons, renamed the Royal College of Surgeons in 1800. In November 1786, Hunter encountered a patient with "a hard swelling of the lower part of the thigh, as it were beginning from the knee. Hunter described an "osteoid sarcoma" of the distal femur (A) and also noted the intramedullary spread of the tumor: "A short distance below the site of amputation there is a second hemispherical tumour in the medullary canal. Hunter noted that "when the leg was amputated he had not the least symptom of any disease in the chest" but deduced that the lung metastases "had taken place a considerable time before the symptoms took place. In patients with nonresectable primary tumors, such as difficult pelvic bone sites, vertebral column, frontal bones, or base of skull, and in patients who refuse definitive surgery, consideration should be given to precision high-dose irradiation. Modern photon techniques use three-dimensional computerized treatment planning and intensity-modulated radiation therapy.
Only 10% of patients who sustain pelvic fractures have an associated bladder injury rheumatoid arthritis headache buy voltaren with amex. Several studies analyzed the location and site of pelvic fracture and the relative risk of bladder injury. In their review of bladder ruptures, Sivit and colleagues101 identified 7 children, and only 4, or 57%, had pelvic fractures compared with 89% in adults. This increased incidence of bladder rupture in the absence of pelvic fracture is the result of the more exposed position of the bladder above the pelvic ring in children. The hallmark signs of bladder injury are suprapubic pain and tenderness, inability to urinate, and gross hematuria. All patients with bladder injury have significant microhematuria, and gross hematuria occurs in 95%. Of patients with the findings of pelvic fracture and gross hematuria, 45% have bladder rupture. This accounts for the high mortality of 20% to 40% in patients with bladder rupture. A, A modified Boari flap may be created by tabularizing a wide-based flap of bladder and rotating it toward the shortened ureter. B, the bladder may be moved closer to the ureter by shifting its position in the pelvis to the injured side and sewing it to the psoas muscle with a psoas bladder hitch. Bladder contusion is described as damage to the bladder mucosa or muscle without loss of bladder wall continuity or extravasation of urine. Most contusions manifest with hematuria, and the diagnosis depends on a thickened or irregular appearance of the bladder wall on imaging. Contusions account for one third of all bladder injuries and are treated with catheter drainage alone. It is unnecessary to image the bladder after the catheter is removed if the patient voids normally. Bladder ruptures are described as either intraperitoneal or extraperitoneal, and differ in the site of injury, mechanism of injury, and treatment. Intraperitoneal bladder rupture is more common in children because of the more exposed position of the bladder. The filled bladder is struck, and the acute increase in pressure caused by the trauma against the closed bladder neck causes the bladder to rupture at its weakest and most mobile point, the dome. The dome of the bladder is covered only by peritoneum, and a forceful tear in this area results in a communication with the peritoneal cavity. The diagnosis is made when the cystogram reveals contrast fluid within the peritoneal cavity classically outlining loops of bowel. Intraperitoneal bladder rupture often produces abnormal serum chemistries, including potassium, sodium, nitrogen, and creatinine. In a series of 22 children treated for traumatic bladder rupture, 44% were diagnosed immediately, and 56% had delayed diagnosis after 24 hours. Patients with intraperitoneal bladder ruptures and late presentation had increased serum levels of blood urea nitrogen, creatinine, and potassium. Patients with intraperitoneal bladder ruptures who presented early had increased creatinine and potassium. The accepted management of intraperitoneal bladder rupture is open surgical exploration and primary repair. This is considered an urgent procedure and includes irrigation of the peritoneal cavity. The peritoneal cavity is not drained, but the bladder is drained with either a suprapubic tube or a urethral catheter. Historically, suprapubic tube drainage has been the standard of care when the bladder is repaired from either blunt or penetrating injury, but more recent data have indicated that urethral catheters provide equally effective drainage and fewer complications resulting in shorter periods of diversion. The second type of bladder rupture is extraperitoneal, and it occurs in the lower half of the bladder and is almost exclusively associated with pelvic fractures.
Note that the more proximal branches of the lingular bronchi are normal caliber (arrowheads) rheumatoid arthritis nodules buy discount voltaren 100 mg online. Note the lingula bronchus is not dilated for the first two subsegmental branchings (arrowheads), but is dilated more distally (arrow). However, with mediastinal lung herniation there are intervening pleural layers in the pulmonary isthmus whereas horseshoe lung involves fusion of the posterior basilar segments of the lower lobes. Therefore, intervening pleural layers should not be seen in cases of horseshoe lung and can be used to differentiate it from mediastinal lung herniation. Imaging description Horseshoe lung is a rare congential malformation characterized by fusion of the posterior basilar segments of the right and left lower lobes through a partial parietal pleural defect. Teaching point Fusion of the posterior basilar segments of the lower lobes posterior to the heart on cross-sectional imaging with the absence of intervening pleural layers is diagnostic of horseshoe lung. When horseshoe lung is discovered, careful attention should be paid to the remainder of the chest to exclude associated congential abnormalities. Importance Horseshoe lung itself is usually asymptomatic, however, there are a number of associated abnormalities that may be symptomatic. As stated previously, the most common associated abnormality is Scimitar syndrome. Therefore, when horseshoe lung is identified, careful attention to the remainder of the chest is warranted in an attempt to identify any associated abnormalities. A rare case of horseshoe lung presenting in adulthood and associated with a pulmonary sling: case report and review of the literature. Typical clinical scenario When horseshoe lung is an isolated congential defect it is usually asymptomatic. In symptomatic cases, horseshoe lung is usually diagnosed before one year of age due to pulmonary infection or pulmonary hypertension. There is fusion of the right and left lower lobes posterior to the heart without intervening pleura. Coronal minimum intensity projection image better demonstrates the fusion of the lower lobes medially without intervening pleura. The nodules may coalesce to form conglomerate masses which result in architectural distortion of the lung. Calcification is often present in the nodes and is often amorphous, but can rarely be peripheral (egg-shell). Areas of air trapping can be seen on expiratory imaging in the majority of cases [1]. Additional presentations of pulmonary sarcoidosis include consolidation, cavitation, and fibrosis, but these are less common. Differential diagnosis the imaging findings of sarcoidosis in the chest are usually diagnostic. If the perilymphatic distribution of the nodules is not apparent then pneumoconioses such as silicosis, coal workers, and berylliosis as well as granulomatous infection and metastases are in the differential. Teaching point Recognition of the perilymphatic distribution of the nodules should allow the diagnosis of sarcoidosis to be made in the appropriate clinical setting. Importance Sarcoidosis is a systemic granulomatous disease of unknown etiology that commonly affects the lungs. It typically occurs in young adults, but can be seen in older individuals as well [3]. Typical clinical scenario About half of patients are asymptomatic and discovered incidentally on chest radiographs for other indications. Axial image shows bilateral micronodules in a perilymphatic distribution, most marked in the peribronchovascular regions (arrows). Emphysema can occasionally be mistaken for a cystic lung disease, however, the lack of a wall and the presence of centrilobular core structures (arterioles) within the cystic spaces should allow differentiation [3]. Order voltaren on line amex. My Arthritis Miracle.
|