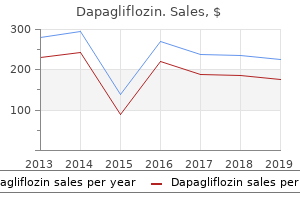
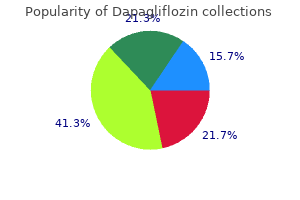
Dapagliflozin"Generic dapagliflozin 5mg visa, diabetes mellitus signs and symptoms of hyperglycemia". By: B. Milok, M.B.A., M.D. Vice Chair, David Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA Delirium is rare with modern obstetric management but should still be considered in the differential diagnosis blood sugar not going up 10 mg dapagliflozin free shipping. Suspiciousness, concealment and impulsivity are common features of puerperal psychosis; hence the risks to both mother and baby are considerable. The clinical priority is to ensure the safety of both mother and baby and so psychiatric admission, ideally to a psychiatric mother and baby unit, is usually necessary. Pharmacological treatment reflects the clinical picture; antipsychotic medication is almost always indicated, augmented by antidepressants if the picture is of psychotic depression and/or by mood stabilisers if the picture is bipolar. Most women recover but the risk of recurrence following subsequent deliveries is 50% and some women will progress to psychotic episodes not associated with childbirth, usually bipolar disorder. It refers to the deliberate and conscious simulation of signs of disease and disability for an identifiable gain (patients have motives that are clear to them but which they initially conceal from doctors). Examples include the avoidance of burdensome responsibilities (such as work or court appearances) or the pursuit of financial gain (fraudulent claims for benefits or compensation). Malingering can be hard to detect at clinical assessment but is suggested by evasion or inconsistency in the history. It can usually be differentiated from postpartum blues by the duration and severity of the symptoms, in particular anhedonia (loss of capacity for pleasure) and negative thoughts. Risk factors include a previous history of depression, a previous history of post-partum depression, antenatal depression and antenatal anxiety. Unlike depression arising at other times, post-partum depression is not more common in lower socioeconomic groups; the prevalence is similar across all social backgrounds. The usual psychological and drug treatments for depression should be considered (p. The potential risks to both mother and child should be considered and, if hospital admission is required, it should ideally be to a mother and baby unit. Psychiatry is similar to other branches of medicine in the applicability of common and case law but differs in that patients with psychiatric disorders can also be subject to legislative requirements to remain in hospital or to undergo treatments they refuse, such as the administration of antipsychotic drugs to a patient with acute schizophrenia who lacks insight and whose symptoms and/or behaviour pose a risk to himself/herself or to others. It is important for practitioners to be familiar with the relevant provisions that apply in their jurisdictions and are likely to arise in the clinical settings in which they work. In general, the guiding principle in British law is that people should be free to make their own decision about any proposed medical treatment, except where their ability to make and/or communicate that decision is demonstrably impaired (by mental illness or physical incapacity). Any restrictions or compulsions applied should be the minimum necessary, they should be applied only for as long as is necessary, and there should be a benefit to the patient m. Safe refeeding management of anorexia nervosa inpatients: an evidence-based protocol. Pharmacological interventions for people with depression and chronic physical health problems: systematic review and meta-analyses of safety and efficacy. Global burden of disease attributable to mental and substance use disorders: findings from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010. Ideally, women with major mental disorders such as bipolar affective disorder should be offered expert pre-conception advice to help them make informed decisions about medication and other aspects of their psychiatric care. A comprehensive post-partum risk management plan should be agreed during pregnancy. Alopecia areata m oo oo eb oo ks oo 8 Detailed morphology of individual lesions Use a magnifying lens in good lighting to assist Use correct terminology (see definitions throughout text) 9 Examination of scalp Hair loss Scalp changes ks fre. This is a mistake; take a history, then examine the skin and the rest of the patient. Define type of lesion using correct terminology Helps in differential diagnosis and allows colleagues to visualise the process. There are more than 50 types of keratin and their expression varies by body site, site within the epidermis and disease state. As keratinocytes migrate from the basal layer, they differentiate, producing a variety of protein and lipid products. Keratinocytes undergo apoptosis in the granular layer before losing their nuclei and becoming the flattened corneocytes of the stratum corneum (keratin layer). Terminal differentiation of keratinocytes relies on the keratin filaments being aggregated and this is, in part, mediated by filaggrin.
Excluding infants with chromosome abnormalities diabetes pathogenesis of type 2 diabetes mellitus safe 5mg dapagliflozin, a prospective analysis of 102,728 pregnancies (including abortions, stillbirths and livebirths) in Texas found that the incidence of congenital malformations increased significantly and progressively in women after 25 years of age. A previous fetus or child with a genetic disorder A genetic evaluation and counseling are usually indicated when a previous fetus or child has or had a genetic disorder, unless the matter is straightforward. Failure or delay in the diagnosis of a monogenic disorder leaves the parents without the option of prenatal diagnosis in a subsequent pregnancy. In addition, it deprives them of the option of preimplantation diagnosis for those disorders with known mutations. Failure to make an early diagnosis of a genetic disorder during the first 5 years of life is common. For example, the Rotterdam Clinical Genetics Group reported that 50 percent of children affected by neurofibromatosis had been treated for related symptoms before a specific diagnosis had been made. Frequently, distressed parents will select a different physician for a subsequent pregnancy and a new or more recent insight may shed light on the cause of the previous disorder. Confined placental mosaicism may also be associated with intrauterine growth restriction,276 requiring serial ultrasounds during the pregnancy. Given the heterogeneous nature of genetic disease, being alert to alternative mechanisms of causation will on occasion be rewarding. Although nonpaternity is more likely, a judicious approach would also include consideration of uniparental disomy. The establishment of the molecular basis of recognized syndromes, previously undetectable prenatally, now provides new opportunities for couples seeking prenatal diagnosis. Examples abound and include some of the craniosynostosis syndromes, certain skeletal dysplasias and many other disorders. In one of our cases, a father with metaphyseal dysplasia of Schmid, troubled by the indignities and hurts of growing up with severe short stature, elected prenatal diagnosis at a preconception visit. Subsequent mutation analysis of conceived twins yielded a normal prenatal diagnosis result confirmed postnatally. The longestablished prenatal diagnosis for both presymptomatic and symptomatic neurodegenerative disorders continue to be expanded to include disorders such as amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and even frontotemporal dementia, by analysis of the C9orf72 22 Genetic Disorders and the Fetus gene. For example, a parent with tuberous sclerosis and normal intelligence could not be certain that an affected child would not have intellectual disability. This was especially evident in our series of 50 couples having prenatal diagnosis for tuberous sclerosis. Certain genetic disorders may (i) threaten maternal health in pregnancy, (ii) threaten fetal health and survival, or (iii) be aggravated by pregnancy. Genetic disorders that threaten maternal health Advances in medical care have resulted in more women affected by genetic disorders surviving to childbearing age and becoming pregnant. There are several genetic disorders affecting the mother that can be aggravated and worsened during pregnancy. Awareness of these disorders facilitates better preconception anticipatory guidance and expectant management during pregnancy. Metabolic disorders that may worsen include ornithine transcarbamylase deficiency, homocystinuria, acute intermittent porphyria, and lysinuric protein intolerance. Hyperammonemia during pregnancy/delivery or postpartum coma may be the presenting signs of a female heterozygote with ornithine transcarbamylase deficiency. Sophisticated and multidisciplinary care and counseling are necessary for women with Marfan syndrome. Pregnancy care: r All appropriate information that would have been reviewed in the preconception period should be discussed if counseling was shortly after pregnancy was established. Labor and delivery: r Planned delivery should occur in hospitals with available cardiac surgery and neonatal intensive care unit facilities. Caution should be exercised in using epidural anesthesia because of the often associated dural ectasia and/or the presence of scoliosis. Postpartum: r Women should be advised about the continuing risk of aortic dissection in the postpartum period with attention to all matters covered in previous counseling. Current recommendations suggest greatest therapeutic efficacy by combining a beta blocker with losartan to reduce the rate of aortic root dilatation. Women with short stature and Marfan syndrome appear to have an increased risk of aortic dissection and hence elective surgery would need earlier consideration. Order dapagliflozin online pills. How Long Does It Take To Get Rid Of Yeast Infections.
There is evidence of short- to medium-term benefit for strong opioids in low back pain and osteoarthritis but there have been very few good-quality studies of long-term use blood glucose monitor buy dapagliflozin mastercard. Additionally, there is increasing concern about potential harm from long-term use. This includes addiction, dependence, opioid-induced hyperalgesia, endocrine dysfunction, fracture risk (especially in the elderly), overdose and cardiovascular re ks f ok s ks fre. There is evidence that doses of more than 120 mg morphine equivalents per day are associated with increased harm, and regular review to assess ongoing benefit is needed in this patient group. The mechanisms are incompletely understood, although endorphin release may explain, in part, m co. There are a range of ways in which psychological therapies can be delivered, including individual one-to-one sessions, group sessions, multidisciplinary pain management programmes, or web-based or telephone-based programmes. The overall aim is to reduce negative thoughts and beliefs, and develop positive coping strategies. The interaction between thoughts, behaviours and emotions is explored, and a problem-focused approach is used in therapy delivery. Acupuncture is particularly effective in pain related to muscle spasm, with some evidence of short-term benefit for patients with low back pain. Neuromodulation, using implanted electrodes in the epidural space (or, more recently, adjacent to peripheral nerves), has been shown to be an effective option for neuropathic pain, including failed back surgery syndrome and chronic regional pain syndrome (see below). Specialist assessment and ongoing support is necessary, as there are many potential complications, including infection, malfunction and battery failure. The likelihood of success is increased when this technique is used within the context of multidisciplinary assessment and management. Assess suitability for opioids Neuropathic pain less likely to respond History of substance or alcohol misuse, including stimulant misuse Avoid use in conditions where adverse effects more likely: Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease Chronic liver disease Chronic kidney disease fre. Grapefruit may also increase the risk of serotonergic effects with some antidepressants. If these are being considered, they should form part of a multidisciplinary management plan, with the aim of restoring function and reducing pain. Local anaesthetic with or without depot glucocorticoid (non-particulate for neuraxial administration) can be effective in some circumstances. Examples include occipital nerve blocks for migraine or cervicogenic headache and trigger point injections for myofascial pain. If there is limited compression of a spinal nerve root, the nerve root injections into the epidural space may help settle symptoms and avoid the need for surgical intervention. Neurodestructive procedures can also be employed for intractable pain but are rarely used outside the palliative care setting. Neuropathic pain may be acute, such as in sciatica, which occurs as the result of a prolapsed disc, but is most problematic when it becomes chronic. The diagnosis is easily missed and so careful assessment is vital, in order to make the diagnosis in the first place and then to direct management appropriately. It is important to recognise the negative impact of neuropathic pain on quality of life, which has been shown to be greater than with other types of chronic pain. As a result, appropriate support and multidisciplinary management should always be considered in addition to pharmacological therapies. It is a rare syndrome, occurring in about 20 per 100 000 individuals, and is more common in females, typically presenting between the ages of 35 and 50. Prompt diagnosis and early treatment with physiotherapy may prevent progression of symptoms. Management is as for neuropathic pain, additional approaches including graded motor imagery. Bisphosphonates have been used empirically for treatment but the evidence base for efficacy in controlling pain is weak. If medical management is incompletely effective, consideration should be given to the appropriateness of a spinal cord stimulator. Reproduced from Murray m Phantom limb is a common complication of amputation, occurring in up to 70% of patients.
Females must have a negative pregnancy test before diabetic diet during pregnancy order dapagliflozin 5 mg, during and after therapy, and pregnancy must be avoided for 2 months after stopping isotretinoin and 2 years after stopping acitretin. Antibiotics re sf re sf sf re Antibiotics are generally used for their anti-infective properties, particularly for staphylococcal and streptococcal skin infections. In these indications, the correct antibiotic should be selected, based on bacterial sensitivity and patient factors. As examples, oral flucloxacillin may be indicated for clinically infected eczema, intravenous flucloxacillin for cellulitis, and clarithromycin for a patient with a staphylococcal carbuncle who is penicillin-allergic. Optimal therapeutic doses and courses must be chosen, based Systemic glucocorticoids, particularly prednisolone, are widely used in inflammatory skin diseases, such as eczema, immunobullous disease and connective tissue disorders. Methotrexate, azathioprine and mycophenolate mofetil are effective in eczema and psoriasis either alone or as glucocorticoid-sparing agents. Further details on the mechanism of action, adverse effects and monitoring requirements for these agents are provided on page 1004, although it is important to be aware that there may be different approaches to treatment regimens and doses between specialties for some drugs. For example, in dermatology, methotrexate is used in a once-weekly regimen, with doses of up to 25 mg per week, depending on the response (p. Hydroxycarbamide is an alternative immunosuppressant to methotrexate in psoriasis, but appears to be less effective and the risk of myelosuppression is greater. For diseases in which histamine in the skin is relevant (such as urticaria), non-sedating antihistamines should be given: for example, fexofenadine or cetirizine. For pruritic conditions such as eczema, the sedating effect of antihistamines like hydroxyzine or chlorphenamine is important. However, antihistamines are widely used in older patients for the symptom of pruritus due to a variety of causes such as xeroderma, metabolic impairment, malignancy or concomitant drugs. Sedating antihistamines should be used with caution in older patients, as they may increase the risk of falls and accidents in the home, with disastrous consequences. Leukotriene receptor antagonists, such as montelukast, may be added to antihistamine regimes. Several antibiotics, such as tetracyclines, erythromycin and co-trimoxazole are used predominantly for their anti-inflammatory effects in indications such as acne vulgaris, bullous pemphigoid and pyoderma gangrenosum. More details on the dosages, mechanism of action and adverse effects of these agents are provided on page 1006. Omalizumab, a monoclonal antibody directed against immunoglobulin E (IgE), was introduced for allergic asthma but may also have a role in non-allergic diseases, such as treatment-resistant urticaria (pp. Intravenous immunoglobulin, pooled from donor plasma, may be used in the treatment of dermatomyositis (p. Cryotherapy Cryotherapy is a destructive treatment using liquid nitrogen to cause cell-wall and membrane destruction and cell death. Liquid nitrogen can be applied either with a cotton bud or, more effectively, with a spray gun. A wide variety of conditions can be treated but it is essential for the correct diagnosis to be made first, if necessary by diagnostic biopsy. Malignant indications require more vigorous treatment, usually with two cycles, and this is normally carried out in secondary care. Considerable inflammation, blistering and pigmentary change, particularly hypopigmentation, can occur. Caution is required to avoid damage to tendons and nerves, especially when using cryotherapy on digits. Dapsone is an immunomodulator and may be used in diseases in which neutrophils are implicated, such as dermatitis herpetiformis (p. Haemolysis, methaemoglobinaemia and hypersensitivity can occur, and monitoring is required (pp. More details on the mechanism of action, adverse effects and monitoring requirements are provided on page 1005. The lesion and line of excision should be marked out and the margin of excision decided before the procedure. Knowledge of local anatomy is essential, particularly the locations of vessels and nerves.
|