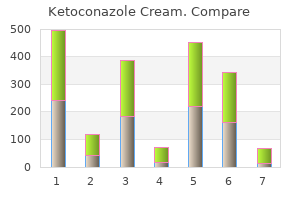
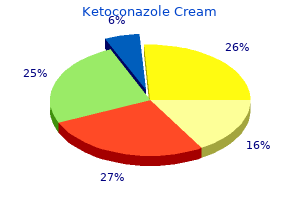
Ketoconazole Cream"Purchase ketoconazole cream 15gm fast delivery, antibiotics for dogs amoxicillin". By: U. Thorek, M.B. B.A.O., M.B.B.Ch., Ph.D. Medical Instructor, Ponce School of Medicine Associated anorexia antibiotic breastfeeding order ketoconazole cream visa, nausea, vomiting and pyrexia Colicky abdominal pain, associated with vomiting and nil passed per rectum. Perforation will cause signs of peritonism Epigastric or right upper quadrant pain (colicky or stabbing). Involve gastroenterologists Urine dipstick, urine for culture Blood cultures, urine dipstick and culture, renal ultrasound scan Urine dipstick (microscopic haematuria), urine for culture, renal ultrasound scan Increase oral intake of fluid, antibiotics Antipyretics, i. Use of prognostic scoring systems Gastroenteritis Generalized, usually crampy abdominal pains, associated with diarrhoea and vomiting Fluids, manage at home if possible (Continued) Investigations and Imaging 147 Hepatitis Right upper quadrant/epigastric pain. May be associated with jaundice Peritonism, may be associated with bowel obstruction Generalized pain, associated diarrhoea, mucus and rectal bleeding, vomiting, weight loss Very rare. Ruptured liver capsule, splenic artery aneurysms, aortic aneurysms, cause haemorrhagic shock and abdominal pain Often thrombosis of right/left iliac vein, causing groin tenderness, leg swelling, sometimes pyrexia Generalized abdominal pain, associated with being systemically unwell Associated with bruising. Domestic violence commonly results in abdominal trauma during pregnancy Right lower lobe pneumonia may cause right upper quadrant pain. Check for other injuries Chest x-ray, blood gases, inflammatory markers, sputum cultures Anticoagulation using low molecular weight heparin, involve haematologists, may require filter in inferior vena cava Treatment dependent on cause, involve the general physicians Ensure safety, specialist mid-wifery service, social input Systemic causes. To put this into context, these are much lower than a long-haul intercontinental flight that provides a 15 mrem dose of radiation, and a short haul flight that provides 6 mrem. Hence, detailed descriptions are given only for significant conditions not discussed elsewhere. As different types of radiation have a different impact on the human body, the dose equivalent is used in order to allow meaningful comparisons of damage. Physiological dilatation of the renal collecting system occurs in pregnancy due to a combination of compression and smooth muscle relaxation secondary to progesterone. Signs helpful in the differentiation of physiological from pathological obstruction have been suggested. In physiological dilatation, the ureter will taper to a normal calibre as is crosses the pelvic brim, but in pathological dilatation, this is lost. Fetal risks, thought to be maximal with exposure between 8 and 15 weeks, are not increased by exposures less than 5 rad. As previously discussed, diagnosis is often hampered due to the physiological effects of pregnancy. Ultrasound is useful, although less so during the third trimester, or if the appendix has perforated. As a result, approximately 40 per cent of pregnant patients who undergo appendicectomy have a normal appendix. Management of appendicitis is surgical, and involving general surgical colleagues early is recommended. Surgery can be open, using an incision over the point of maximal tenderness (may be right paramedian or midline in late pregnancy), or laparoscopic. Laparoscopic surgery is now considered acceptable during pregnancy, even during the third trimester. Reports in the literature describe veress needle insertion either in the mid-clavicular line, 2 cm below the inferior costal margin, or the open Hasson technique. The open Hasson entry technique is recommended as it avoids insufflation of the uterus which would be catastrophic to the fetus. In cases in which there is diffuse peritonitis, intravenous antibiotics are recommended pre-operatively. Caesarean section may also need to be considered if the mother is severely unwell, particularly as gestation approaches term. Acute cholecystitis Acute cholecystitis is the second most common surgical cause of an acute abdomen in pregnancy, with an incidence of between 1:1600 and 1:10 000 pregnancies. Over 90 per cent of cases are caused by gallstones, and Differential diagnoses 149 gallstones are an incidental finding in between 3. Purging of bone marrow to remove T lymphocytes is now widely used as a means of reducing the incidence and severity of Monitoring the allograft response Allograft rejection conjures up a dramatic picture of immunological events antibiotics low blood pressure purchase generic ketoconazole cream on line, which should be eminently suitable to monitoring by the examination of peripheral blood for changes in antibody or lymphocyte characteristics. Many attempts, involving a wide range of antibody and lymphocyte assays, have failed to provide a clinically useful means of distinguishing rejection episodes from other events such as infection, or one that gives sufficient warning to be able to modify the outcome by therapeutic intervention. This is due to the fact that the specific cells and antibodies of interest are mostly preoccupied within the graft and thus not available for peripheral sampling. Fine needle aspiration biopsy enables samples (10 l) of renal grafts to be removed on alternate days without significant damage to the 181 Chapter 15 Transplantation graft. The nature of the cellular infiltrate is a useful guide to the development of rejection and its severity: the presence of T and B cell blasts occurs early in the rejection process, and infiltration with monocytes indicates severe and possibly irreversible change. Otherwise, one is left with the non-immunological observation of graft function, using physical, biochemical, isotopic or electrocardiographic techniques and these changes can be very non-specific. Infertility Hair loss Cystitis Non-specific immunosuppression the potency of the anti-allograft response is such that none of the factors cited thus far is sufficient to achieve graft survival without the administration of drugs, which suppress the immune system non-specifically. In allotransplantation most rejection episodes occur during the first 3 months but a reduced level of immunosuppressive treatment is required indefinitely in most cases. In the early days of renal transplantation, immunosuppression was usually achieved using the antiproliferative drug, azathioprine (in a dose of c. It can cause bone marrow aplasia and frequent monitoring of the white cell count is required. Corticosteroids probably have an effect on T-cell function 182 Osteoporosis Avascular bone necrosis Cataracts Myopathy Hypercholesterolaemia Hypertension Hepatotoxicity in addition to their anti-inflammatory effect on phagocytic cells. It does, however, have several important side effects including nephrotoxicity, hirsutism, gum hypertrophy, hypercholesterolaemia, hypertension and hepatotoxicity, most of which are dose-related. It has similar side effects to cyclosporin with the exception of hirsutism and gum hypertrophy. Mycophenolate mofetil is gradually replacing azathioprine in immunosuppressive regimens as it is more effective in preventing acute rejection and is less toxic than azathioprine. It is a more specific and potent inhibitor of T and B cell proliferation due to its inhibition of purine biosynthesis. However, serious infection has been a problem in some patients treated with these preparations and this emphasizes the overall limitation of non-specific immunosuppression. Opportunistic infection is still a major cause of death in most transplantation programmes and emphasizes the need for more sophisticated forms of immunosuppression. The small but significant increase in the incidence of lymphomas and skin tumours is due to impaired immunity to oncogenic viruses. The subject of secondary immunodeficiency is discussed in more detail in Chapter 11. Specific immunosuppression the prospect of inducing antigen-specific immunosuppression at will in the adult animal has been the goal of transplantation immunology since the 1950s when Medawar and his colleagues were able to induce a similar state in neonatal mice. Experiment 2 shows that if cells from strain A mice are inoculated into newborn mice of strain B then the latter animals accept skin grafts derived from strain A throughout their adult life having become specifically tolerant of this histocompatibility type. That the tolerant animals are immunologically normal apart from their specific unresponsiveness to allografts from strain A is demonstrated in experiment 3 in which the natural tendency to reject the strain A graft the animal already bears is restored by the infusion of cells from a strain B animal that has not been pretreated with strain A cells when newborn. Many other attempts have been made to induce immunological tolerance in adult animals and often with considerable success but the means by which graft acceptance has been achieved have not usually been clinically applicable or acceptable. It has been known for many years that the administration of graft-specific antibody can promote graft acceptance although there is always a risk of hyperacute rejection. This phenomenon of antibody-mediated enhancement has been studied extensively and, at one stage, received limited clinical application for renal transplantation. In experiments where prolonged graft acceptance has been achieved by this means it is clear that the initial phase of induction (or passive enhancement) achieved by antibody is replaced by a maintenance phase (of active enhancement) in which other mechanisms operate. Enhancement can also be actively induced by the administration of allogeneic cells or cell extracts prior to transplantation. These experiments were first performed by Billingham, Brent and Medawar (Billingham et al. When successful, the animals bearing enhanced grafts tend to show a progressive unresponsiveness to the donor strain. Purchase cheap ketoconazole cream on-line. Olga Tosas-Auguet: Mapping bacterial antibiotic resistance.
Most of the margin is well defined antibiotics for uti in pregnancy order ketoconazole cream 15gm fast delivery, but mild irregularity and lobulation of the superficial margin are present (arrows). Two sentinel lymph nodes (arrows) are identified after injection around the tumor illustrated in. Both of these nodes were removed, and no metastatic disease was identified histologically. If there is a significant invasive ductal component, then the margins may be ill defined or spiculated. Metaplastic carcinoma of the breast: mammographic appearance with pathologic correlation. The septations within the mass have color flow, and the edge of the mass consists of solid tissue that forms an ill-defined margin (arrows). One mass is in the upper outer quadrant, and the other is in the outer inferior quadrant. Imaging findings in mucin-containing carcinomas of the breast: correlation with pathologic features. The lump was first detected 1 year ago and had been found to be sonographically solid. The palpable mass corresponds to a well-defined, oval solid mass with heterogeneous echogenicity and increased acoustic transmission. This tumor most frequently metastasizes to lungs (66%), skeleton (28%), and lymph nodes (15%). They are similar to fibroadenomas, but they should be considered if the mass is > 6 to 8 cm or is rapidly growing. Unlike fibroadenomas, phyllodes tumors commonly have thin, irregular cystic spaces within them. Phylloides tumor: findings on mammography, sonography, and aspiration cytology in 10 cases. Although the tumor has been reported in a wide age range (17 to 75 years), it tends to present in younger women (average age in the 30s). Stamford: Appleton and Lange; 1999:697 Irregular Masses this is an outline of the approach to mammographic irregular masses. The palpable mammographic mass corresponds to a hyperechoic oval mass, which has a partially ill-defined margin. The palpable mammographic mass corresponds to an ill-defined irregular mass with a hyperechoic rim and hypoechoic center. In some patients, the fat necrosis causes a fibrotic response that results in an irregular solid mass (illustrated in this case), which may be associated with skin thickening and nipple retraction. This mass cannot be distinguished mammographically or sonographically from carcinoma. Besides producing an irregular mass, fat necrosis may also produce a lipid collection without an inflammatory response. This second type of fat necrosis results in a round or oval nodule (oil cyst) that is either calcium or fat density mammographically. In the upper outer quadrant, the new small spiculated mammographic mass corresponds to an ill-defined hypoechoic shadowing mass. The hyperechoic halo around the mass corresponds to the mammographic spiculations.
However bacteria zone of inhibition discount ketoconazole cream 15gm overnight delivery, if a scar develops a hypoechoic mass from fibrosis or fat necrosis, then malignancy cannot be excluded. This lesion most commonly presents as a palpable mass in patients 50 to 70 years old. Myofibroblastoma of male breast: report of three cases and review of the literature. There are multiple areas of abnormal uptake in the ribs, spine, and right hip consistent with metastatic bony disease. The lower percentage has been reported in Japan and the higher percentages in the United States and Scandinavia. However, if the surgeon wishes to obtain a breast biopsy prior to excision, then one may perform a sonographically guided biopsy may be appropriate as these lesions are generally easily identified with this method. Benign causes include congenital position, duct ectasia, subareolar abscess, granulomatous mastitis, and postoperative scarring. The size of the main sonographic mass matches the mammographic size (approximately 2. However, if one adds the length of the abnormal ducts, the total length of the abnormality is 5 cm. The sonographically dilated ducts histologically corresponded to dilated ducts with infiltrating carcinoma within the walls. To confirm this information, sonographically guided biopsies of both the mass and the abnormal ducts were performed. Both the biopsies and the excisional specimen confirmed that the tumor size matched the sonographic size. She now presents for needle localization of these microcalcifications before lumpectomy. These calcifications are associated with a dumbbellshaped ill-defined mass (arrows). The shape of this mass and the sub- C tle multinodular pattern of the surrounding parenchyma suggest that the tumor may be multifocal. This mass corresponds to the mammographic mass containing the microcalcifications. Mastectomy specimen: grossly, the tumor was 4 cm, but random sections outside this mass demonstrated small foci of infiltrating and in situ ductal carcinoma, so the overall size of the malignancy could not be defined. Multicentricity refers to the simultaneous development of multiple different malignancies. Usually, a tumor is considered multifocal if the foci are either within the same quadrant of the breast or within 5 cm of each other. Sometimes, with multiple oblique magnification views, one can identify spiculations extending from one mass to another. The medial inferior abnormality (A) is not confidently identified during an attempt to perform mammographic stereotactic biopsy and is not localized on the initial breast sonogram. Lesion B exhibits low-intensity clip artifact from previous mammographic stereotactic core biopsy. Due to differences in pathologic examination and definition of multicentricity, studies have reported the prevalence of multicentricity as between 9 and 75%. Invasive ductal carcinoma has a lower rate of multicentricity (19%) compared with other histologies.
|