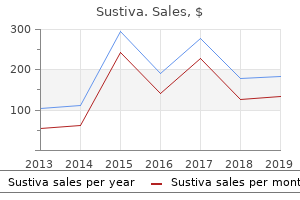
Sustiva"Cheap 200mg sustiva mastercard, symptoms you have worms". By: M. Mirzo, MD Clinical Director, Oakland University William Beaumont School of Medicine There is a need for standardized tests that accurately measure plasma concentrations and anticoagulant effects medications band buy sustiva online now. Other disadvantages are possibly higher rates of gastrointestinal hemorrhage and greater expense than with warfarin. The presence of an atherosclerotic stenotic lesion in the extracranial internal carotid artery or carotid bulb has been associated with an increased risk of stroke. However, the risk of stroke in patients undergoing intensive contemporary medical treatment has fallen significantly since the mid-1980s. However, the advantages of the surgical intervention have also been shown in subgroups of patients with diabetes. Pooled analysis of these trials, including more than 3000 symptomatic patients, found a combined 30-day stroke and death rate of 7. Patients with a moderate (50% to 69%) stenosis who are at reasonable surgical and anesthetic risk may benefit from an intervention performed by a surgeon with excellent operative skills and a perioperative morbidity and mortality rate of less than 6%. Diabetes was the strongest independent predictor of restenosis or occlusion after both procedures, with a 2. In patients with stenosis with a degree greater than 50%, no indication for carotid revascularization exists. Beyond 30 days, stroke in the same brain territory occurred in 13 patients in each group. The frequency found in various studies depends on the following: 1 the definition of the threshold of hyperglycemia (fasting glucose from 6. After an initial peak, blood glucose levels were lower approximately 14 to 16 hours later; this was followed by a second hyperglycemic peak 48 to 69 hours later. In this context, repeated episodes of severe hypoglycemia are thought to contribute to the development of cognitive decline and dementia, because of their cumulative neurotoxic effect (see the later discussion of diabetes as a vascular risk factor for cognitive impairment and dementia). Acute hypoglycemia provokes profound physiologic changes affecting the cardiovascular system and several hematologic parameters, as a consequence of sympathoadrenal activation and counter-regulatory hormonal secretion. Many of these responses have an important role in protecting the brain from neuroglycopenia, through altering regional blood flow and promoting metabolic changes that will restore blood glucose to normal. Some of these effects are potentially pathophysiologic, and in people with diabetes who have not yet developed endothelial dysfunction, they may have an adverse impact on a vasculature that is already damaged. The acute hemodynamic and hematologic changes may increase the risk of localized tissue ischemia, and major vascular events can certainly be precipitated by acute hypoglycemia. The possible mechanisms underlying these hypoglycemia-induced cerebrovascular effects include hemorrheologic changes, white cell activation, vasoconstriction, and the release of inflammatory mediators and cytokines. Therefore it is suggested that acute and repeated hypoglycemia could aggravate cerebrovascular complications associated with diabetes by enhancing atherosclerotic vascular and proembolic changes. There are contradictory endocrinologic findings in reference to the "stress postulates" because some studies could not prove the claimed stress metabolism. These have shown that there is not one singular damage mechanism, but rather there are a coaction and an interaction of various "neurotoxic" effects. Table 28-9 summarizes the potential direct and indirect mechanisms of neuronal damage by hyperglycemia during the acute phase of ischemic stroke. In patient studies, the negative prognostic impact of hyperglycemia was identified after adjustment for other variables such as age, severity, and extent of the stroke. Even more recent studies, such as one conducted at the Mayo Clinic,96 found that glucose levels of more than 7. After multivariable statistical adjustment, any hyperglycemia above this limit value was associated with a risk of unfavorable progression that was 2. This correlation could be demonstrated not only in larger but also in smaller infarctions. Finally, the presently available evidence is contradictory in terms of the significance of isolated increased glucose levels compared with continuous increases. Because of the uncertainty of its benefit-risk ratio in patients with diabetes, thrombolysis is often withheld in many such patients. Hence, outcomes with thrombolysis are better than controls among patients with diabetes, indicating no statistical justification for the exclusion of patients with diabetes who are otherwise eligible from receiving thrombolytic therapy in acute ischemic stroke. Glucose-Lowering Treatment of Poststroke Hyperglycemia Feasibility of Glycemic Control in Poststroke Hyperglycemia There is no consensus regarding the best type of glycemic control, the best method for achieving it, and the necessary monitoring in the setting of acute stroke. One study from Glasgow involving 13 patients105 showed the basic feasibility of a strict decrease in increased values by approximately 1 to 2 mmol/L with only one observed hypoglycemic event.
The authors of this study did not mention whether the women were consuming aluminum-containing medications medications that cause tinnitus purchase 600 mg sustiva visa, and the measured levels are apparently the normal baseline for the patient population studied. In a surveillance study of Michigan Medicaid recipients involving 229,101 completed pregnancies conducted between 1985 and 1992, 183 newborns had been exposed to sucralfate during the 1st trimester (F. Specific data were available for six defect categories, including (observed/expected) 1/2 cardiovascular defects, 1/0 oral clefts, 0/0 spina bifida, 1/0. A population-based observational cohort study formed by linking data from three Swedish national healthcare registers over a 10-year period (19952004) was reported in 2009 (12). The drug types included in the study were gastric acid suppressors, including H2receptor antagonists, prostaglandins, proton pump inhibitors, combinations for eradication of Helicobacter pylori, and drugs for peptic ulcer and gastroesophageal reflux disease, such as sucralfate. The authors proposed three possible mechanisms for their findings: (a) exposure to increased amounts of allergens could cause sensitization to digestion labile antigens in the fetus; (b) maternal Th2 cytokine pattern could promote an allergy-prone phenotype in the fetus; and (c) maternal allergen-specific immunoglobulin E could cross the placenta and sensitize fetal immune cells to food and airborne allergens. Several limitations of the study that might have affected their findings were identified, including a general increase in childhood asthma but not necessarily an increase in allergic asthma (12). Aluminum, barium, silicon, and strontium in amniotic fluid by emission spectrometry. Although no reports describing the use of the narcotic during the 1st trimester have been located, the lack of teratogenicity in animals and the general opinion that narcotic agents, in general, pose little risk of congenital malformations are reassuring. Sufentanil rapidly crosses the placenta to the fetus, even more so in the presence of fetal acidosis, and similar to all narcotics, doserelated depression of the fetus and newborn may occur. Both respiratory depression and adverse effects on neonatal neurobehavior are potential problems in the newborn. If sufentanil is used in pregnancy, healthcare professionals are encouraged to call the toll-free number (800-670-6126) for information about patient enrollment in the Motherisk study. No evidence of teratogenicity has been observed in rats and rabbits, but the drug was embryocidal (most likely due to maternal toxicity) in both species when it was given for 1030 days in a dose 2. No adverse reproductive (number of implantations and live fetuses, percent fetal wastage per litter, or mean fetal weight) or teratogenic effects (major or minor malformations) were observed in rats administered continuous infusions of sufentanil at doses of 10, 50, or 100 mcg/kg/day from day 5 through day 20 of pregnancy (2). The placental transfer of sufentanil was studied in an experiment using the dual-perfused, single-cotyledon human placental model at doses of 1, 10, 20, and 100 ng/mL (3). Sufentanil was shown to rapidly cross the placenta by passive diffusion, but high maternal protein binding significantly reduced this transfer, whereas progressive fetal acidemia (reduction in pH from 7. Placental tissues appeared to bind sufentanil, but this accumulation apparently did not affect the overall net drug transfer to the fetus. In another in vitro study, a single-pass (open) placental perfusion model was used to assess the placental transfer of sufentanil (1 and 100 ng/mL) and the effect of maternal plasma proteins, placental metabolism, and fetal pH (7. The conclusions of this study were identical to those of the study above, in that sufentanil rapidly crossed the placenta by passive diffusion, the placenta acted as a depot for the narcotic, maternal protein binding (not albumin) decreased transfer, and fetal acidosis increased the amount reaching the fetus (4). The authors also concluded that because of its low initial transfer (umbilical vein concentration only 2% of maternal concentration at 5 minutes), sufentanil may be the narcotic of choice if delivery is imminent (<45 minutes) (4). Sufentanil crosses the placenta to the fetal circulation following maternal epidural anesthesia (5,6). In a 1991 double-blind study, 60 women undergoing elective cesarean section at term were randomized to receive epidural anesthesia consisting of 0. The mean plasma concentrations of sufentanil in the mother and newborn in the 20-mcg group (14 subjects) were 0. The placental transfer of sufentanil, fentanyl, and bupivacaine was studied in a double-blind, randomized trial involving 36 women at term who received epidural anesthesia during labor prior to vaginal delivery (6). Intrathecal sufentanil (10 mcg), followed at least 1 hour later with bupivacaine epidural analgesia (N = 65), was compared with bupivacaine epidural analgesia alone (N = 64) in a 1996 report comparing the effects of the two analgesic regimens on fetal heart rate changes during labor (7). No statistical differences were observed between the groups in the incidence of clinically significant fetal heart rate tracing abnormalities (recurrent late decelerations and/or bradycardia) or in maternal hypotension within the 1st hour of administration (7). In addition, there were no differences between the groups in arterial or venous cord pH or the number of 5-minute Apgar scores <7. No abnormal fetal heart rate patterns were observed in an earlier study that compared intrathecal sufentanil (10 mcg) either alone (N = 20) or with 0. Epinephrine did not prolong analgesia but did increase the incidence of vomiting while decreasing the incidence and severity of pruritus.
Density of apoptotic nuclei surrounding the necrotic core was significantly greater in individuals with type 1 and type 2 diabetes as compared with those without diabetes treatment leukemia buy sustiva 200mg on line. The effects of hyperglycemia on both endothelial cells and macrophages are most pronounced in the presence of an inflammatory environment. This effect could be blocked by superoxide dismutase enzyme of bisindolylmaleimide-I, thus showing the importance of oxidative stress in hyperglycemia. Hernбndez Vera et al55 showed that lean normoglycemic rats transplanted with diabetic rat bone marrow had increased thrombosis with normal glucose levels, whereas diabetic rats transplanted with lean normoglycemic control bone marrow showed reduced thrombosis despite the presence of hyperglycemia. Rats with increased thrombosis had significantly greater platelet volume, activated and reticulated platelets, increased turnover and production of platelets, reduced expression of platelet-endoplasmic reticulum stress proteins (protein disulfide isomerase and 78-kDa glucose-regulated protein), and increased tissue factor procoagulant activity, as compared with lean normoglycemic controls. Levin L, Tomer Y: the etiology of autoimmune diabetes and thyroiditis: evidence for common genetic susceptibility, Autoimmun Rev 2:377386, 2003. Late result of actual 10-years follow-up in 376 patients, Jpn J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 47:110115, 1999. Gyongyosi M, Yang P, Hassan A, et al: Coronary risk factors influence plaque morphology in patients with unstable angina, Coron Artery Dis 10:211219, 1999. Roguin A, Koch W, Kastrati A, et al: Haptoglobin genotype is predictive of major adverse cardiac events in the 1-year period after percutaneous transluminal coronary angioplasty in individuals with diabetes, Diabetes Care 26:26282631, 2003. Motoyama S, Kondo T, Sarai M, et al: Multislice computed tomographic characteristics of coronary lesions in acute coronary syndromes, J Am Coll Cardiol 50:319326, 2007. Maffei E, Seitun S, Nieman K, et al: Assessment of coronary artery disease and calcified coronary plaque burden by computed tomography in patients with and without diabetes mellitus, Eur Radiol 21:944953, 2011. Diabetes-induced coronary artery disease is associated with greater inflammatory infiltrate (macrophages and T lymphocytes), larger necrotic core size, and diffuse atherosclerosis. Further studies are needed to better understand the relationship of hyperglycemia and insulin resistance that lead to acceleration of atherosclerosis. Makita Z, Vlassara H, Cerami A, et al: Immunochemical detection of advanced glycosylation end products in vivo, J Biol Chem 267:51335138, 1992. Vedantham S, Noh H, Ananthakrishnan R, et al: Human aldose reductase expression accelerates atherosclerosis in diabetic apolipoprotein E-/- mice, Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 31:18051813, 2011. Hernandez Vera R, Vilahur G, Ferrer-Lorente R, et al: Platelets derived from the bone marrow of diabetic animals show dysregulated endoplasmic reticulum stress proteins that contribute to increased thrombosis, Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 32:21412148, 2012. The latter occurs both secondary to myocardial infarctions and as a result of innate diabetes-mediated damage to the myocardium. With the worldwide rise in both types 1 and 2 diabetes, an epidemic of cardiovascular complications in diabetes is almost certainly on the horizon. Hence, it is essential to delineate the diabetes-specific mechanisms that accelerate cardiovascular disease to identify the optimal therapeutic regimens to combat these heterogeneous diseases. Hyperglycemia is both defining and common to types 1 and 2 diabetes, yet there are common and distinct threads in these two syndromes. The potential underlying mechanisms linking diabetes and cardiovascular complications may differ, at least in part, between these two most common forms of diabetes. Specifically, insulin resistance is significantly more common in type 2 diabetes, but it may appear in later stages of type 1 diabetes as well. Furthermore, hyperinsulinemia is more associated with type 2 diabetes, because type 1 diabetes, at least in the absence of therapies, is caused by a reduction in naturally produced and circulating insulin. In this chapter we review the evidence supporting, or not, the roles of hyperglycemia, hyperinsulinemia, and insulin resistance in cardiovascular complications. Note that this chapter does not consider in depth the influences of dyslipidemia, inflammation, hypercoagulability, or endothelial dysfunction in diabetes; these are the focus of Chapter 10. Long-term intervention studies have begun to answer the critical question of whether strict control of hyperglycemia imbues protection or at least reduction in cardiovascular consequences in diabetes. Specifically, of the adolescents, the mean age of subjects randomized to either arm of strict versus standard glycemic control was age 15 years (a total of 87 patients). Of the adults, the mean age of patients randomized to either arm of glycemic control was age 28 years (a total of 191 patients). Both surrogate markers of atherosclerosis (carotid intima-media thickness) and myocardial infarction, stroke, and death from cardiovascular consequences were shown to be reduced in the group of patients treated with strict versus standard regiments of glucose control. In type 2 diabetes, current epidemiologic data have identified that the overall risk of cardiovascular complications is twofold to fourfold greater than that observed in nondiabetic patients, even after accounting for the traditional risk factors. After 10 years the study showed that levels of glycosylated hemoglobin were significantly lower in the strict control group versus standard (7. There was, however, a nonstatistically significant trend toward lower nonfatal myocardial infarction, nonfatal stroke, or death from cardiovascular causes in those in the glycemic control groups.
Vitamin E in placental blood and its interrelationship to maternal and newborn levels of vitamin E medicine youtube purchase sustiva overnight delivery. Red blood cell tocopherol concentrations in a normal population of Japanese children and premature infants in relation to the assessment of vitamin E status. The effect of nutrition in teenage gravidas on pregnancy and the status of the neonate. Vitamin E deficiency: a previously unrecognized cause of hemolytic anemia in the premature infant. Difference in plasma- and red blood cell-tocopherols in, breastfed and bottle-fed infants. Vitamin E concentrations in serum of newborn infants after topical use of vitamin E by nursing mothers. Additional studies will be needed to establish whether the protective effect includes only certain types of patients. Until that time, it seems prudent to recommend that folate-containing multivitamin preparations should be used immediately before and during at least the first few months of pregnancy. Preparations containing multiple vitamins (multivitamins) are routinely given to pregnant women. A typical product will contain the vitamins A, D, E, and C, plus the B-complex vitamins thiamine (B 1), riboflavin (B2), niacin (B3), pantothenic acid (B5), pyridoxine (B6), B12, and folic acid. Miscellaneous substances that may be included are iron, calcium, and other minerals. The practice of supplementation during pregnancy with multivitamins varies from country to country but is common in the United States. Deficiencies of vitamins may also be teratogenic (see individual vitamin monographs for further details). The role of vitamins in the prevention of certain congenital defects continues to be a major area of controversy. An investigation into a third class of anomalies, limb reduction defects, has also appeared. Animal research in the 1930s and 1940s had shown that both deficiencies and excesses of selected vitamins could result in fetal anomalies, but it was not until two papers in 1958 (2,3) that attention was turned to humans. The treated group, composed of 39 women, received multivitamins plus injectable B-complex vitamins during the 1st trimester. This work was further expanded, and the total group involving 645 pregnancies was presented in a 1976 paper (8). Of the total group, 417 women were not given supplements during pregnancy, and they gave birth to 20 infants (4. In the treated group, 228 women were given B-complex vitamins plus vitamin C before or during the 1st trimester. Although suggestive of a positive effect, the difference between the two groups was not significant. In contrast, one author suggested that the vitamin A in the supplements caused a cleft palate in his patient (10). Thus, the published studies involving the role of multivitamins in the prevention of cleft lip and/or palate are inconclusive. No decisive benefit (or risk) of multivitamin supplementation has emerged from any of the studies. The differences between the case mothers and the controls were significant for red blood cell folate (p <0. Based on this experience, a multicenter study was launched to compare mothers receiving full supplements with control patients not receiving supplements (1619). The supplemented group received a multivitaminironcalcium preparation from 28 days before conception to the date of the second missed menstrual period, which is after the time of neural tube closure. The daily vitamin supplement provided: Their findings, summarized in 1983, are shown below for the infants and fetuses who were examined (19): Although the numbers were suggestive of a protective effect offered by multivitamins, at least three other explanations were offered by the investigators (16): 1. Although multivitamin supplements were not studied, it was assumed that those patients who consumed adequate diets also consumed more vitamins from their food compared with those with poor diets. The above investigations have generated many discussions, criticisms, and defenses (2457). The primary criticism centered on the fact that the groups were not randomly assigned but were self-selected for supplementation or no supplementation.
In a 2009 case (see Fetal Risk Summary) symptoms 7 dpo bfp order sustiva 200mg with mastercard, a mother taking ziprasidone and citalopram breastfed her full-term infant for 6 months. No adverse effects were noted and the infant was deemed healthy by his pediatrician (2). Consistent with the molecular weight of the free base (about 413) and the elimination half-life (up to 7 hours), ziprasidone is excreted into breast milk but, as suggested by the very high plasma protein binding (>99%), only low levels were excreted. However, the absorption of ziprasidone in adults is increased twofold in the presence of food (1). Although no adverse effects were observed in one case, additional data are needed before a better assessment of risk can be made. Moreover, because treatment with ziprasidone will usually be long term, there is concern for potential adverse effects involving the neurobehavior of an infant. Ziprasidone and citalopram use in pregnancy and lactation in a woman with psychotic depression. Animal reproduction data suggest risk, but the absence of human pregnancy experience prevents a more complete assessment of embryofetal risk. However, ziv-aflibercept is given in combination with two other antineoplastics and the three agents potentially could cause embryo fetal harm. In addition, ziv-aflibercept has caused reversible impaired fertility in male and female cynomolgus monkeys at systemic exposures that were less than those obtained in humans. Moreover, the manufacturer recommends that females and males of reproductive potential should use highly effective contraception during treatment and up to a minimum of 3 months after the last dose (1). It is indicated, in combination with 5-fluorouracil, leuvovorin, and irinotecan, for patients with metastatic colorectal cancer that is resistant to or has progressed following an oxaliplatin-containing regimen (see also Fluorouracil, Irinotecan, and Leuvovorin). The metabolism and plasma protein binding were not specified, but the elimination half-life of free ziv-aflibercept was about 6 days (range 47 days) (1). These effects included increased incidences of postimplantation losses and external (anasarca, umbilical hernia, diaphragmatic hernia and gastroschisis, cleft palate, ectrodactyly, and atresia), visceral (great vessels and arteries in the heart), and skeletal fetal anomalies (fused vertebrae, sternebrae, and ribs; supernumerary arches and ribs, and incomplete ossification). In females, the drug inhibited ovarian function and follicular development as shown by decreased ovary weight, amount of luteal tissue, and number of maturing follicles; atrophy of uterine endometrium and myometrium, vaginal atrophy, abrogation of progesterone peaks and menstrual bleeding. In males, alterations in sperm morphology and decreased sperm motility were noted. All of these effects were reversible within 18 weeks after cessation of therapy (1). The molecular weight (about 115,000) suggests that it will not cross, at least early in gestation, but the elimination half-life is very long. Moreover, the drug did cause embryofetal toxicity in rabbits during organogenesis. The molecular weight (about 115,000) suggests that it will not be excreted into mature milk, but it probably will be excreted during the colostral period. However, the drug is given in combination with 5-fluorouracil, leuvovorin, and irinotecan (see also these three agents) and the two antineoplastic agents are probably excreted into breast milk. Consequently, breastfeeding should be considered contraindicated if a woman is receiving this combined therapy. The animal data suggest risk, but the limited human pregnancy experience prevents a complete assessment of the embryofetal risk. The amount of zoledronic acid incorporated into bone and eventually released back into the systemic circulation is directly related to the total dose and duration of treatment. Because zoledronic acid probably crosses the placenta, the use of the drug shortly before or during gestation could expose the embryo and/or fetus to a potentially toxic agent. The use of zoledronic acid in women who may become pregnant or during pregnancy is not recommended. Other agents in this pharmacologic class are alendronate, etidronate, ibandronate, pamidronate, risedronate, and tiludronate. Other adverse fetal effects observed in the high-dose group were reduced lens, rudimentary cerebellum, reduction or absence of liver lobes, reduction or absence of lung lobes, vessel dilation, cleft palate, and edema, but maternal toxicity (reduced body weight and food consumption) also was observed (1). Maternal toxicity (dystocia and periparturient mortality) was observed at all exposures 0. This toxicity was thought to be secondary to drug-induced inhibition of skeletal calcium mobilization, resulting in hypocalcemia, a bisphosphonate class effect (1). Order sustiva overnight. Withdrawal Symptoms of Smoking.
|